A Look Inside The Growing U.S. Market Landscape For Surgical Navigation & Robotics
By Donna Santos and Kamran Zamanian, Ph.D., iData Research
Surgical navigation and robotic systems are not novel technologies and have had a historical presence since the 19th century. Surgical navigation is a result of evolution from a frame-based stereotaxy technology. David Robert first developed the concept of frameless stereotaxy for neurosurgery.1 Several studies have demonstrated the efficacy of surgical navigation in improving accuracy. Its function is usually compared to a GPS-like tracking system, allowing surgeons to visualize the position on a map and to consolidate and integrate data from various sources such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans.
Furthermore, it was in 1985 that the first surgical application using robotic technology occurred when a robotic arm was modified to perform a brain biopsy.2 The first robot to assist in surgery that received FDA clearance is the AESO,3 approved in 1994, followed by the da Vinci surgical system in 1997.4 The increase in dexterity, accuracy, and flexibility, combined with enabling an improved ergonomic position, is one of the advantages of using robotic-assisted surgery (RAS) systems.
Adoption Of Surgical Navigation And RAS Systems
In neurosurgery, computer-assisted surgery (CAS), or image-guided surgery (IGS), has become the standard of care. Moreover, in spine surgeries, less than 30% of the combined thoracolumbar spinal fixation and posterior cervical spinal fixation procedures use surgical navigation systems. Though the use of surgical navigation in other clinical applications depends on the complexity of the procedure to be performed, overall, the adoption of CAS in orthopedic and ENT procedures was slow in the past years.5
The adoption rate of RAS systems in orthopedics is significantly higher compared to that in surgical navigation, exceeding it by more than threefold in 2023.6 Furthermore, in minimally invasive surgery, the procedures in which the use of RAS systems is widely adopted include general surgeries and gynecology and urology procedures. On the contrary, only a small fraction of neurosurgery and spine surgeries used robotic systems in 2023.
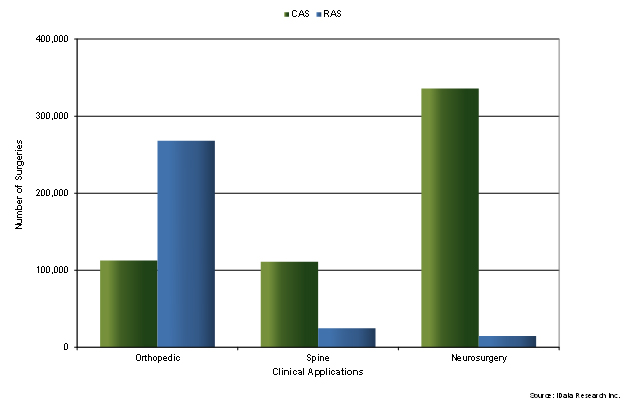
Figure 1: Number of Procedures using CAS and RAS in Orthopedic Spine and Neurosurgery Surgeries, U.S., 2023.
Market Growth
The rapid growth rate of surgical navigation per clinical application varies, with orthopedic surgical navigation having the fastest growth rate while neurosurgery navigation systems have the slowest growth rate due to market saturation.
In robotics, the number of capital equipment systems placed grew by double digits from 2020 to 2023. With the increasing adoption of surgical robotics systems bolstered by the increasing demand for procedures, it is projected that a strong double-digit growth rate will persist until 2030.
Overall, the market valuation of both surgical navigation and robotics, comprising the capital equipment in outright purchases, disposables, and other accessories and service and maintenance revenue market segments, will grow from $6.9 billion in 2023 to $18.9 billion in 2030.
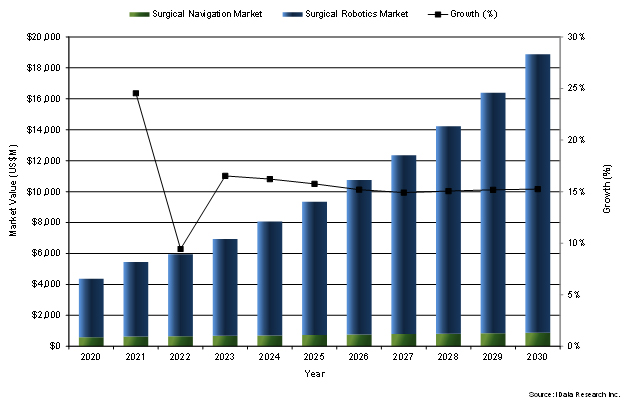
Figure 2: Surgical Navigation and Robotics Market, U.S., 2020-2030 (US$M).
Market Propellers And Limiters
Studies have demonstrated that procedures performed using navigation systems and robotic systems across medical fields result in more accurate surgeries. Particular benefits include reducing the surgical team’s exposure to radiation, better outcomes, surgery time reduction, and fewer complications and revisions during surgery. This reduces the length of stay for patients, resulting in cost savings.
In addition, the clinical and economic benefits of robotic systems are tied to their ability to do minimally invasive procedures, leading to better outcomes and fewer complications and revisions during surgery. This reduces the length of stay for patients, resulting in cost savings.
Manufacturers and distributors offering leasing or other flexible financial arrangements enable more hospitals and ambulatory surgery centers to adopt surgical navigation and robotic systems. Generally, navigation systems are less expensive for healthcare providers/hospitals to buy (ranging from $100,000 to $400,000) compared to robotic systems (ranging from approximately $650,000 to $4 million). This is particularly beneficial for those institutions that recognize the clinical and financial advantages of surgical navigation and robotics systems but have limited capital investment budgets.
Furthermore, as market competition intensifies, products are being developed at lower costs. One emerging technology that fuels the ASP decline is augmented reality (AR)-based surgical navigation systems. While adopting this technology may increase unit sales, it has an impact on the ASP of other types of surgical navigation systems with auxiliary screens, contributing to a minimal drop in the overall market value of the combined markets. Consequently, this downward pressure will help more hospitals and ambulatory surgery centers to adopt and upgrade their technology. Moreover, virtual reality and augmented reality technologies have been starting to gain interest and are being widely adopted by many surgeons as part of their training and surgical education, facilitating the simulation of procedures. With that in mind, an AR-based surgical navigation system will be easier for the new generation of surgeons to use, providing real-time guidance without the need to look at an external screen during surgery.
Market Leaders In The Surgical Robotics Market In 2023
Here are the top companies that have gained traction in the overall surgical robotics market (not in any particular order).
- Intuitive Surgical
Intuitive Surgical is one of the leading competitors in overall surgical robotics owing to its dominance in the minimally invasive surgery robotic system market. The company offers a portfolio of surgical instruments and robotic systems such as da Vinci Si, da Vinci Xi, and da Vinci X which can be used in various clinical indications. Intuitive Surgical has strengthened its dominance in the market as it received FDA clearance of its da Vinci 5The da Vinci 5 three-dimensional (3D) display and image processing, and force feedback technology that Intuitive claims is something not being offered by any surgical technology from competitors.
- Stryker
Stryker is one of the leading competitors in the orthopedic robotic system market. The company entered the robotic-assisted surgery market after its acquisition of MAKO Surgical Corp in 2013. Its product, Mako system, has applications for partial knee arthroplasty (PKA), total knee arthroplasty (TKA), and total hip arthroplasty (THA). The number of procedures performed with the Mako robotic application in the U.S. showed a threefold increase in 2018 from 2016. In May 2021, the company announced that Mako had been used in over 500,000 procedures, a number that will double by 2024.
In January 2021, Stryker announced the acquisition of OrthoSensor, a company leading in sensor technology for joint replacements. OrthoSensor offers its intraoperative sensor, VERASENSE, which has been used alongside Stryker products since 2011.
- PROCEPT BioRobotics
PROCEPT BioRobotics secured a position among the top companies in the overall surgical robotic system market due to its market share in other MIS capital equipment market segments. PROCEPT BioRobotics is a private surgical robotics company based in the United States. The company markets the AquaBeam Robotic System, enabling robotic-assisted aquablation therapy – resection and removal of prostate tissue – to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia. The AquaBeam Robotic System received FDA clearance in December 2017. Aquablation therapy can provide effective, durable, and safe outcomes for men suffering from lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTSs) caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), regardless of the prostate size and shape or even the surgeon’s experience.
In 2024, PROCEPT BioRobotics reported that it has 400 installed robotic systems in the United States.7 The company continues to contribute to surgical robotics innovation and aquablation therapy: in August 2024, PROCEPT BioRobotics announced that it received its FDA clearance for its HYDROS Robotic System. It features FirstAsisst AI, which is built from a library of aquablation therapy and boosts its robotic resection capability by utilizing a heat-free waterjet.
- Medtronic
Medtronic dominated the surgical navigation market with its StealthStation S8 and StealthStation ENT in 2023, and the company has been continuously strengthening its brand recognition in the market. Medtronic is another major player in the overall surgical robotics market in the U.S., thanks to its product Mazor
Medtronic also entered the robotic-assisted MIS market in 2021 by launching its MIS robotic-assisted platform, Hugo RAS. Currently, Hugo RAS is an investigational device and is not yet for sale in the United States, but it has obtained a Health Canada license and CE mark for specific clinical indications. Medtronic’s solid reputation in the medical device market will likely help the company occupy a strong position in the surgical robotics market in the near future.
- Smith & Nephew
Another competitor that has a huge impact in the orthopedic robotic system market is Smith & Nephew. Its NAVIO and CORI surgical systems are strong competitors of Stryker’s Mako in the orthopedic robotic system market. Unlike Stryker’s Mako system, Smith & Nephew’s CORI is not limited to exclusive use with Smith & Nephew’s implants and has the widest range of compatible implants for TKA and PKA.
In March 2019, the company announced that it acquired Brainlab’s orthopedic joint reconstruction business. Brainlab’s orthopedic-specific software includes the RI.KNEE NAVIGATION, RI.HIP NAVIGATION, and TRAUMACAD solutions, sold by Smith & Nephew. Smith & Nephew manufactures the AchieveCAS navigation system for use during total knee and total hip arthroplasties. The company’s NAVIO and CORI robotic platforms allow it to be present in two competing technologies. Furthermore, in January 2022, Smith & Nephew announced its expansion of its CORICORI
- Johnson & Johnson
In 2023, DePuy Synthes, a company of Johnson & Johnson, was a major player in the total surgical robotics market owing to its market share in the robotic-assisted orthopedic surgery market. In January 2021, the company received FDA clearance for its VELYS Robotic-Assisted Solution, designed to be used alongside the ATTUNE Total Knee System for knee procedures. In addition to knee procedures, the system can be used for hip and shoulder procedures. VELYS Robotic-Assisted Solution was first used in Australia in December 2021. To further enhance the abilities of its orthopedic robot, DePuy Synthes acquired CUPTIMIZE Hip-Spine Analysis in March 2022. The tool is intended to assist surgeons in understanding and addressing the effect of irregular motion between the spine and the pelvis in select patients who require a THA. In October 2019, DePuy Synthes announced a collaboration with Tinavi Medical Technologies to promote its robotic solutions for spinal and other trauma surgeries in China.
Auris Health, previously known as Auris Surgical Robotics, is another subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson’s company, acquired in 2019 through Ethicon. Auris Health markets the Monarch platform, a robotic flexible endoscope that received FDA clearance for diagnostic and therapeutic bronchoscopic procedures in March 2018. The first surgery using Monarch was performed in the U.S. in April 2018. Auris is also planning to enter the MIS market through its iPlatform robot, which will compete with Intuitive Surgical’s da Vinci. However, the ownership of Verb Surgical, its joint venture with Verily, contributed a complication. In 2024, Johnson & Johnson was ordered to pay more than $1 billion in damages to Auris for breaching the terms of its acquisition agreement, but it is considering appealing the judgment.
References
- Mezger, Uli, et al. “Navigation in Surgery.” Langenbeck’s Archives of Surgery, vol. 398, no. 4, 22 Feb. 2013, pp. 501–514.
- Hockstein, N. G., et al. “A History of Robots: From Science Fiction to Surgical Robotics.” Journal of Robotic Surgery, vol. 1, no. 2, 17 Mar. 2007, pp. 113–118.
- George, Evalyn I., et al. “Origins of Robotic Surgery: From Skepticism to Standard of Care.” JSLS: Journal of the Society of Laparoendoscopic Surgeons, vol. 22, no. 4, 2018, p. e2018.00039
- “FDA Clearance of Da Vinci Surgical System for Intracardiac Surgery Now Encompasses ``ASD’’ Closure | Intuitive Surgical.” Isrg.intuitive.com,
- “Surgical Robotics and Navigation Market Size, Share & Covid-19 Impact Analysis: United States: 2022-2028: MedSuite: Includes: Neurosurgery Navigation Market, Spinal Surgical Navigation Market, and 10 More.” iData Research, November 2, 2022. Accessed May 7, 2024.
- Mako SmartRoboticsTM hits 500,000+ procedures. (n.d.). Stryker.
- FDA Clears PROCEPT BioRobotics’ HYDROS Robotic System. (2024, September 11). Medical Product Outsourcing.
About The Authors:
Donna Santos is a research analyst at iData Research, specializing in the surgical navigation and robotics, dental prosthetics, and digital dentistry markets. She has years of experience as a marketing analyst and a bachelor’s degree in engineering and a postgraduate diploma in data analytics.
 Kamran Zamanian, Ph.D., is CEO and founding partner of iData Research. He has spent over 20 years working in the market research industry with a dedication to the study of medical devices used in the health of patients all over the globe.
Kamran Zamanian, Ph.D., is CEO and founding partner of iData Research. He has spent over 20 years working in the market research industry with a dedication to the study of medical devices used in the health of patients all over the globe.
