Breast Reconstruction In The U.S.: Procedure Preferences & Market Trends
By Kateryna Hronska and Kamran Zamanian, iData Research
Breast cancer survival rates have experienced a notable increase, prompting a shift in focus from mere survival to the enhancement of quality of life. The American Cancer Society estimated approximately 300,000 new breast cancer cases in 2023.1 Mastectomy, a procedure involving the removal of breast tissue, is a common practice for both treatment and prevention purposes. Recent advancements in mastectomy techniques have led to refinements, rendering the procedures less intrusive. Post-mastectomy, breast reconstruction plays a vital role in improving psychosocial well-being and body image. The trend of immediate breast reconstruction following mastectomy is on the rise, aimed at expediting recovery. Furthermore, bilateral mastectomy, the removal of both breasts, is increasingly favored for preventive measures or achieving aesthetic symmetry.
The realm of breast reconstruction encompasses two main approaches: implant-based and autologous tissue procedures. While autologous procedures may pose complications related to tissue removal, innovative techniques such as the free transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) flap have alleviated some associated risks. Acellular dermal matrices are frequently used in implant-based reconstruction, facilitating implant coverage and yielding favorable long-term aesthetic outcomes. Conversely, alloplasts are seldom employed due to concerns regarding scarring in breast tissue. Mesh reinforcement primarily serves to mitigate the risk of herniation in TRAM flap procedures.
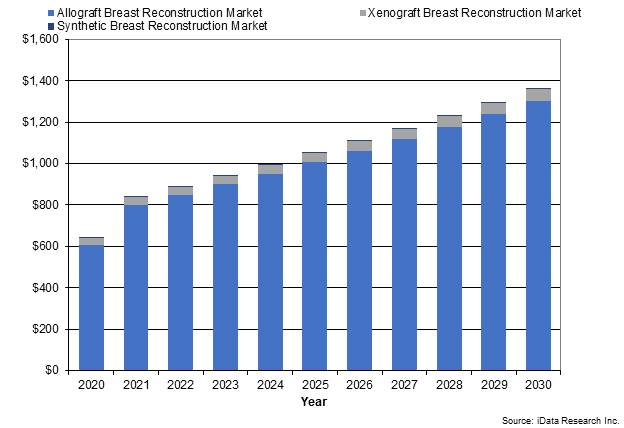
This article focuses on three segments of the breast reconstruction market: allografts, xenografts, and synthetics. Allografts are preferred for their superior mesh properties, including higher elastin content, which enhances stretch characteristics crucial for achieving aesthetically pleasing results desired by patients. Additionally, allografts boast a favorable clinical track record, resulting in better long-term outcomes and higher patient satisfaction compared to xenografts and synthetics.
Xenografts, while representing a smaller portion of the market, have shown inferior results compared to allografts due to their decreased stretch characteristics and subpar aesthetic outcomes, leading to a decline in popularity in recent years.
Similarly, synthetics have a minimal presence in the market, with no indication of significant future growth.
Implant-based breast reconstruction remains the industry standard due to the established popularity of implant devices and robust clinical data supporting their advantages. However, challenges such as implant rupture, scar tissue formation, and the need for consistent monitoring by healthcare professionals exist. Conversely, autologous or flap breast reconstruction, although less common due to its procedural complexity, offers an alternative method using tissue transplanted from another part of the body to form the breast shape.
Allograft
Breast reconstruction allografts, derived from human tissue, are widely used in breast reconstruction procedures, serving various essential functions. Firstly, they offer crucial structural support to the reconstructed breast, aiding in its shaping and contouring, thus ensuring a natural appearance. Secondly, allografts play a pivotal role in providing coverage and support to implants in implant-based reconstruction, contributing significantly to achieving a desirable and realistic outcome. Furthermore, these allografts contribute significantly to the overall aesthetic enhancement of the reconstructed breast, promoting symmetry and improving its appearance, which is essential for patient satisfaction.
The use of breast reconstruction allografts comes with notable benefits. Allografts offer a natural feel and appearance, surpassing synthetic materials, thereby enhancing patient satisfaction significantly. Derived from human tissue, allografts pose a reduced risk of rejection compared to synthetic alternatives. They facilitate improved healing outcomes post-reconstruction by promoting tissue integration.
However, it's essential to acknowledge potential complications associated with their use. Allografts may elevate the risk of infection, particularly if not adequately sterilized or if an immune response is delayed. Some patients may experience immunologic reactions to allografts, leading to inflammation or rejection.
Cost considerations are noteworthy, as allografts might incur higher expenses compared to synthetic materials, potentially impacting the overall cost of breast reconstruction procedures. Availability of suitable allografts may pose challenges, contingent upon tissue donor availability and specific tissue matching requirements.
In 2023, the allograft breast reconstruction market constituted the vast majority of the total market, and it is expected to be the fastest growing over the forecast period. AbbVie is one of the top competitors in the allograft market. The company’s dominance in this segment is due to its AlloDerm allograft product for breast reconstruction, an acellular dermal matrix (ADM).
Xenograft
Breast reconstruction xenografts, derived from non-human tissue, are used in breast reconstruction procedures for various purposes. Firstly, they provide structural support to the reconstructed breast, aiding in shaping and contouring to achieve a natural appearance. Secondly, xenografts can be used to cover and support implants in implant-based reconstruction, contributing significantly to achieving a desirable outcome. As clinical data has accumulated over the years, it has become apparent that allografts exhibit superior performance when it comes to breast reconstruction due to their dermal stretch characteristics and remarkable aesthetic results, whereas xenografts are a better fit for ventral hernia repair due to their exceptional tensile strength characteristics that offer the support needed for abdominal reinforcement. This makes xenografts a good choice for reinforcement of the abdominal wall during a TRAM flap procedure, although alloplasts remain the product of choice for those procedures, due to their substantially lower price. Nevertheless, the xenograft segment is expected to remain relatively stable, mostly due to the fact that these devices are a less expensive option than allografts, and the more competitive price will sometimes outweigh their inferior clinical performance. Xenografts will continue to show slight ongoing increases in unit sales as both the number of tissue expander/implant-based (TEI) procedures and the rate of bilateral reconstructions increase.
Cost considerations are noteworthy, as xenografts may incur higher expenses compared to synthetic materials, potentially affecting the overall cost of breast reconstruction procedures. Availability of suitable xenografts may pose challenges, depending on the source and quality of the tissue. Integra LifeSciences offers the SurgiMend (PRS), a fetal/neonatal bovine dermal collagen matrix xenograft exhibiting biochemical properties to facilitate rapid cell penetration and revascularization. In 2023, the company recalled the product for further endotoxin testing.
Synthetic
Breast reconstruction synthetics, also referred to as alloplasts, are commonly used materials in breast reconstruction surgeries aimed at providing structural support and shaping the breast mound. The advantages of using breast reconstruction synthetics encompass their adaptability and longevity. They can be customized to various shapes and sizes, catering to individual patient requirements, and they yield enduring outcomes. Moreover, synthetics obviate the need for tissue harvesting from alternative body regions, potentially diminishing surgical complications and recovery duration. Nevertheless, there exist potential complications linked to the use of breast reconstruction synthetics. These include the likelihood of infection, implant rupture, capsular contracture (the formation of scar tissue around the implant), and issues like implant displacement or asymmetry. Additionally, some patients may encounter allergic reactions or rejection of the synthetic material.
Conclusion
To sum up, the landscape of breast reconstruction in the United States continues to evolve with advancements in surgical techniques, materials, and patient preferences. Allografts remain the dominant choice due to their superior aesthetic outcomes and clinical success, while xenografts and synthetics play more specialized roles in the market. Despite their distinct advantages, each approach presents its own set of challenges, ranging from potential complications like infections and immune reactions to cost and availability concerns. As the demand for personalized and effective breast reconstruction grows, the focus on improving patient outcomes and satisfaction will drive further innovation, shaping the future of the breast reconstruction market.
Reference
 About The Authors:
About The Authors:
Kateryna Hronska is a senior research analyst at iData Research. She works on research projects regarding the medical device industry, publishing the U.S. Soft Tissue Repair market research report.
 Kamran Zamanian, Ph.D., is CEO and founding partner of iData Research. He has spent over 20 years working in the market research industry with a dedication to the study of medical devices used in the health of patients all over the globe.
Kamran Zamanian, Ph.D., is CEO and founding partner of iData Research. He has spent over 20 years working in the market research industry with a dedication to the study of medical devices used in the health of patients all over the globe.
