Digital Tomosynthesis Leads The Way In Breast Imaging
By Federica Cogoni, MA, and Kamran Zamanian, Ph.D., iData Research
Breast cancer is a significant global health issue, as it is the most common cancer in women worldwide and the second-leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally. In the United States, there are over 250,000 new cases of breast cancer annually, with over 46,000 women dying of the disease.1 When breast cancer is detected early, over 95% of women survive more than five years.2 For this reason, breast imaging diagnostic procedures have been steadily increasing, due to an increased awareness and aging population. However, false-positive results are common, especially in younger women whose breasts are denser, which leads to additional imaging diagnostics via ultrasound and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), or 3D mammography, has become a leading technology in breast imaging, with advances in image reconstruction algorithms and AI integration improving suspicious lesions detection. DBT has demonstrated a moderate reduction in false-positive cases when compared to 2D mammography, or conventional digital mammography.
Breast Imaging Screening Procedures: Overview
In 2023, in the United States, breast imaging procedures, which include mammography procedures, ultrasound procedures, MRI coils, and gamma imaging procedures, have been increasing at a steady rate. Mammography procedures account for a large portion of all breast imaging procedures.
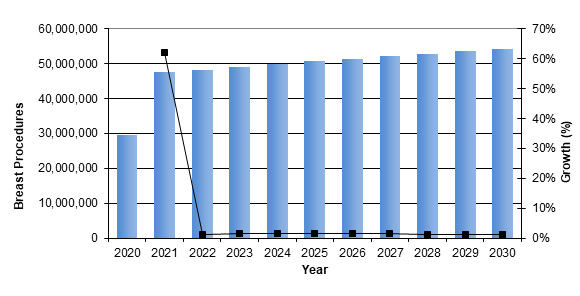
Figure 1: Breast Imaging Procedures Performed from 2020 to 2030.
Access iData’s U.S. Market Report Suite for U.S. Medical Imaging Market.
These procedures are expected to increase year over year, as they are recommended by doctors for cancer prevention. The U.S. Preventive Service Task Force recommends that women aged 50 to 74 years received a mammogram every two years and that women aged 40 to 49 years make an individual decision regarding screening.3
However, screening for cancer and studies of overdiagnosis have shown that false-positive results occurred more frequently for women who underwent annual screening, were younger, and/or had dense breasts.4 A false positive is when a mammogram is flagged as abnormal, but there is no cancer in the breast. To ensure accuracy and avoid false positives, physicians may request additional imaging diagnostic via an ultrasound and MRI, especially in patients with dense breast tissue.
Studies have shown that ultrasounds significantly increase the detection of clinically important, small, largely invasive, and node-negative cancers.5 Screening the ultrasound is effective in detecting mammographically hidden cancer cells in women with dense tissue.
Breast MRI is a high-risk screening, which is recommended annually to supplement a mammogram for women with a personal history of breast cancer and dense breast tissue, as well as when a woman has had a recent breast cancer diagnosis.6 Risk-based screening is based on an individual woman’s risk of developing breast cancer. Depending on a woman’s individualized risk, optimal screening is tailored and may include mammography, ultrasound, and MRI.
A Closer Look At Leading DBT Systems In Breast Imaging
The U.S. breast imaging market is segmented into mammography, breast ultrasound, breast MRI coils and Molecular Breast Imaging (MBI). Each system serves distinct purposes within the realm of breast imaging. Within the mammography market, segmentation consisting of computed radiography (CR) mammography, digital radiography (DR) mammography, and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) further breaks down the market.
In 2023, the DBT market was the largest market within the medical breast imaging market.
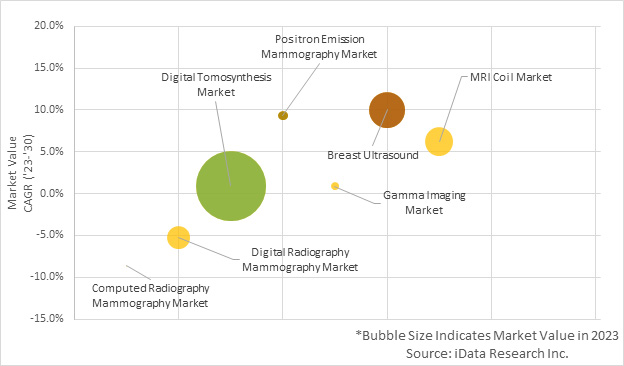
Figure 2: Bubble Chart of Breast Imaging Market Segments in 2023.
Access iData’s U.S. Market Report Suite for U.S. Medical Imaging Market Devices
DBT market value growth is largely attributed by the increase growth rate in units’ sales and ASP positive growth rate over the forecast period. This growth in ASP is primarily driven due to the availability of new technology.
It has been shown that repeated breast cancer screenings with 3D mammography, or DBT, modestly decreases the chance of having a false positive result compared with the standard digital 2D mammography, or conventional digital mammography.7 This factor is driving growth in the number of procedures and the market for digital tomosynthesis devices.
The incorporation of technological advances, such as AI, into digital tomosynthesis systems has enhanced the detection of breast abnormalities. The introduction of AI systems has created a more comprehensive view of the breast tissue through pattern recognition capabilities. Additionally, advances in image reconstruction algorithms have led to sharper and clearer tomosynthesis images, which reduce the effects of artifacts and improve lesion detection. Technological advances such as these have driven market growth. Thanks to these technological advancements, DBT represents the largest segment within the breast imaging market.
DBT has undergone significant advancements since receiving its initial U.S. FDA clearance in 2011 in the form of Hologic’s Selenia Dimensions system in 2011, which offers 3D breast tomosynthesis along with 2D mammography. It also integrates AI technology for image processing.
In 2016, GE Healthcare launched Senographe Pristina Mammography System, the digital mammography system that offered DBT with features like gentle mammogram compression, patient-assisted compression, and AI algorithms for improved workflow.
The Planmed Clarity 3D DBT system was introduced and launched in 2016. The system offers breast tomosynthesis with low-dose imaging and features like patient comfort paddles and synthetic mammography.
In 2017, Siemens Healthineers launched the Mammomat Revelation system, which combined breast tomosynthesis with synthetic mammography and offered personalized compression for enhanced patient comfort.
In 2021, Fujifilm launched the Amulet Innovality system, which features DBT with iterative reconstruction, AI-based image processing, and synthetic mammography capabilities.
Closing Thoughts
Breast cancer stands as a significant global health concern, ranking as the most prevalent cancer among women worldwide and the second most common cause of cancer-related fatalities. In 2023, breast imaging procedures, encompassing mammography, ultrasound, MRI, and gamma imaging, continue to experience a steady rise, driven by awareness and an aging population. Nonetheless, the issue of false-positive results remains pervasive, particularly affecting younger women with dense breast tissue and often necessitating additional ultrasound and MRI diagnostics. Within the realm of breast imaging technology, DBT has emerged as a premier solution. Notably, advances in image reconstruction algorithms and the integration of artificial intelligence have significantly enhanced lesion detection.
References
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures. American Cancer Society; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2021.
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures. American Cancer Society; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2021.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) Breast Cancer Screening accessible: https://progressreport.cancer.gov/detection/breast_cancer#:~:text=In%202021%2C%2075.9%25
%20of%20women,within%20the%20past%202%20years. - Nelson HD, Pappas M, Cantor A, Griffin J, Daeges M, Humphrey L. Harms of Breast Cancer Screening: Systematic Review to Update the 2009 U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation. Ann Intern Med. 2016 Feb 16;164(4):256-67. doi: 10.7326/M15-0970.
- Thigpen D, Kappler A, Brem R. The Role of Ultrasound in Screening Dense Breasts-A Review of the Literature and Practical Solutions for Implementation. Diagnostics (Basel). 2018 Mar 16;8(1):20. doi:
- 10.3390/diagnostics8010020Houser M, Barreto D, Mehta A, Brem RF. Current and Future Directions of Breast MRI. J Clin Med. 2021 Nov 30;10(23):5668. doi: 10.3390/jcm10235668.
- Ho TH, Bissell MCS, Kerlikowske K, Hubbard RA, Sprague BL, Lee CI, Tice JA, Tosteson ANA, Miglioretti DL. Cumulative Probability of False-Positive Results After 10 Years of Screening With Digital Breast Tomosynthesis vs Digital Mammography. JAMA Netw Open.;5(3), doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.2440
 About the Authors:
About the Authors:
Federica Cogoni is a senior research analyst at iData Research. She develops and composes syndicated research projects about the medical device industry in various fields.
 Kamran Zamanian, Ph.D., is CEO and founding partner of iData Research. He has spent over 20 years working in the market research industry with a dedication to the study of medical devices used in the health of patients all over the globe.
Kamran Zamanian, Ph.D., is CEO and founding partner of iData Research. He has spent over 20 years working in the market research industry with a dedication to the study of medical devices used in the health of patients all over the globe.
