Korean GMP: MFDS Requirements For On-Site And Document Audits of Medical Device Manufacturing Plants
By KangKeun (Daniel) Lee, Freyr Solutions

(KGMP) sets minimum standards with which medical device and In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) device manufacturers must comply. It is one of the Quality Management System (QMS) standards that manufacturers must follow to guarantee the quality of medical devices from development through the stages of purchase, inspection, packaging, installation, storage, shipment, and return; it is also required in order to access the Korean market. Currently, it is based on ISO 13485:2016, and conformity assessment is carried out through initial examinations, regular examinations, additional examinations, and change examinations. At the beginning of COVID-19, the on-site audit was temporarily replaced by a document audit, which requires strict and detailed document procedures.1,2 As of January 2023, Korea has switched back to on-site audits, and there is a long waiting list to get an audit date. Due to the different timelines and characteristics of the four KGMP audit organizations, manufacturers should carefully select and apply for the appropriate organization. The Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) provides training and presentation sessions to help industry stakeholders understand the requirements and comply with them.
On-site Conformity Assessment of Medical Devices
The manufacturer is subject to a Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) audit for an initial approval of its manufacturing or import business, and subsequently, to regular reviews every three years to assess the efficacy of the QMS. The GMP review standards and procedures vary with the type of audit being conducted. Before applying for KGMP certification, the manufacturer should determine the type of audit applicable and should prepare for the conformity assessment accordingly. Refer to Table 1 for the types of audits and their respective objectives.2,3
Table 1: Types of KGMP Audits and their Respective Objectives
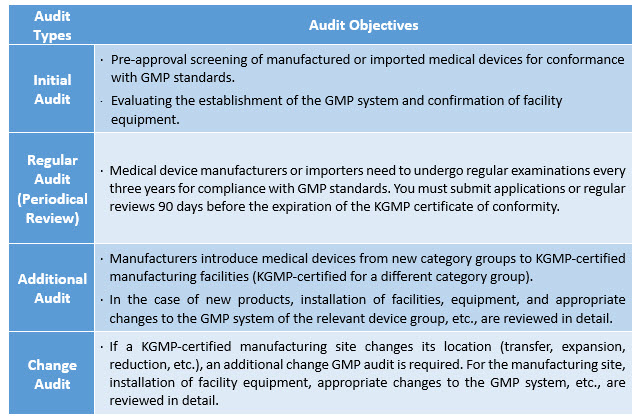
Medical device manufacturers, importers, or companies that wish to manufacture or import medical devices for clinical trials must comply with the KGMP standards. They may select one of the four quality control institutions (KTL, KTR, KCL, or KTC) registered with the MFDS in accordance with the medical device manufacturing and quality control standards (public notice by the MFDS).
In case of an additional category of medical devices or a change of manufacturing site, the manufacturer must apply to the quality management review agency. The medical device officer of the MFDS will either visit the applicant’s company for an on-site audit or carry out a document review.
GMP conformity recognition does not end with the initial screening; rather, it should be reviewed regularly every three years. Manufacturers should file an application for regular audits with a quality control examination agency, following the same procedure as for the initial, additional, or change audits. The manufacturer is responsible for keeping track of the validity period of the KGMP conformity certificate and applying for regular audits 90 days before the expiration of the KGMP certificate.
Foreign manufacturers, like domestic manufacturers, must undergo regular screening, and importers that have multiple foreign manufacturers can submit a comprehensive list of foreign manufacturers and apply for it collectively.
If an importer is handling medical devices manufactured by multiple foreign manufacturers, regular audits will review the products with the highest risk rating, safety, validity problems, or side effects. Only the manufacturer with the maximum number of imported products in the high-risk group will be subject to an on-site review, while the other foreign manufacturers will be subject to a document review.2
Table 2: GMP Review Type
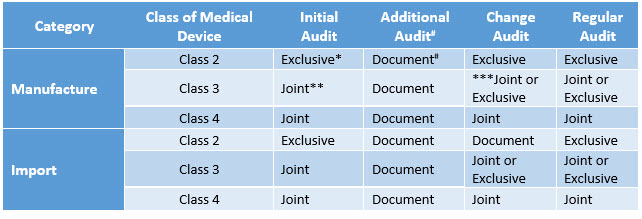
* Exclusive on-site investigation by the quality control review authority.
** Joint on-site audit by the local food and drug administration and the quality control review authority.
*** Joint or exclusive on-site audit if it is a hazardous manufacturing plant (non-conformity of quality in three years).
# Only document review; on-site audit exempted (on-site audit would be considered for the next regular audit).
KGMP Conformity Recognition for Class I Medical Devices
Class I medical devices that pose little risk to the human body are not subject to KGMP review. The medical device manufacturer must observe the KGMP standards in accordance with the Medical Device Act. However, the manufacturer can also opt to undergo a review, such as KGMP conformity recognition of Class I medical devices, which includes a KGMP review, except for some evaluation items. The notable difference between ISO 13485:2016 screening and KGMP is that in KGMP, each item is reviewed through all the manufacturing cycles for a representative model. The selection of the representative item is determined by the following two criteria:
- The representative model is the item with the highest production or import volume as the highest risk class at the relevant manufacturing site. In addition, the manufacturer must submit the basis for selecting the representative model.
- The basis, production, and import volume refer to the data reported to the Korea Medical Devices Industry Association (KMDIA) over the last three years (based on the calendar date).
Document Review of Medical Devices
Conducting only a document review is limited to the following five cases:
- A document review is conducted if the existing GMP-compliant manufacturing plant manufactures additional medical devices in different categories under the condition that the same quality management system is maintained within the expiration date.
- After changing the location of a manufacturing plant, the manufacturer must submit a copy of the QMS conformity certificate (ISO 13485 certificate, etc.) issued by the government of the producing country.
- If another manufacturer/importer has already received a valid certificate of conformity in accordance with KGMP, the examination may be conducted only by reviewing documents. In such cases, the validity period of the certificate of conformity issued because of the examination is calculated in the same manner as the validity period of other manufacturers and importers who have been previously audited. However, in the case of a regular examination, it can be applied only when a valid certificate of conformity of another business operator is issued through an on-site audit.
- If there are two or more manufacturing plants, such as plant A, plant B, and plant C, manufacturing plant A will undergo an on-site audit, and the other manufacturing plants (B and C) will be subject to document audits. However, if an on-site audit is inevitably impossible to be carried out (such as a site of a civil war or an infectious disease epidemic of a level recognized by the MFDS) for manufacturing plant A, one of the other sites (B or C) will be subject to an on-site audit, even if the document reviews of those plants have already been completed.
- If a manufacturer who has received a GMP audit under the In Vitro Diagnostics Medical Device Act is subject to a GMP audit under the Act, the audit may be conducted only by reviewing documents. In this case, the validity period of the certificate of conformity issued as a result of the audit is calculated in the same manner as the validity period of other manufacturers and importers who have been reviewed under the In Vitro Diagnostics Medical Device GMP.
In the following scenarios, manufacturers will have to apply for a new initial audit:
- If a manufacturer or importer voluntarily undergoes a GMP examination for export or Class I medical device manufacturing facilities that are exempt from a GMP examination or a clinical GMP examination, they do not need to undergo a regular examination every three years. In such cases, a new initial examination is conducted.
- If a manufacturer who has already undergone a GMP review of medical devices for export intends to manufacture their product for domestic approval and sale rather than for export, a new initial review is conducted.
- If the relationship between the legal manufacturer and the manufacturer who has already been reviewed for conformity, etc., changes, a new initial examination is conducted.
- If the manufacturer changes the location of the manufacturing facility that has undergone a GMP review for clinical trial medical devices, adds other clinical trial medical devices, or intends to manufacture/import the device for domestic approval and sales, a new initial audit is conducted.
- If a manufacturing/importing company that has undergone a GMP review of a Class I medical device manufacturing plant wants to manufacture/import Class 2, 3, or 4 medical devices from the manufacturing plant, a new initial audit is conducted (per Article 5 [2] [3] of the MFDS’ Medical Device Manufacturing and Quality Control Standards).
Data for Submission of the Conformity Recognition, etc., and the Scope of the Recognition
Previously, KGMP audit application required the manufacturer to submit basic information such as the name and location of the manufacturing plant. However, under the revised requirements, the application should also include additional information such as the correlation of the QMS (see Table 3) and the checklist of documents. In many KGMP screening cases, inadequate information on the relationship of the QMS between the major manufacturing stakeholders has resulted in suspension of review or adjustment of business sites on the day of the actual on-site audit. The MFDS revised the form around the end of 2021 to obtain all the necessary information beforehand and avoid such instances during the audit.3
Table 3: Interrelationship of QMS between Manufacturing Consignment and Trust Companies. The parts in the table in red indicate that the manufacturer outsources some of their processes. Click on table to enlarge.
Data Required to Apply for Conformity Certification
On-site Audits
The applicant needs to submit an overview of the manufacturing plant, including the name of the plant, the address of each facility, and the names of all the manufacturing plants, if there are multiple. During an on-site investigation, they must confirm that the actual location of the manufacturing plant is correct. It is important that they share accurate information, as the same details are reflected in the KGMP conformity certificate. Where there are multiple facilities (workplaces, testing labs, and warehouses) in the same location, all of them may be recorded in one place. The applicant must provide the name, location, scope of manufacture, and name and contact information of the Quality Management Representative (QMR). In addition, they may include a brief introduction and description of the manufacturing plant itself.
Document Review
In the case of an examination that includes only document review, the manufacturer should submit the following seven types of data. Since the factories that are subject to on-site audits can be verified during the audit, the on-site audit manufacturer may not submit additional data.
- Organization Chart of the Relevant Manufacturing Plant: The manufacturer must state the name, role, and relationship of the organization (department) responsible for manufacturing and quality-related tasks. The data can be presented in a schematic manner to indicate the connection between the performance of duties, the organizational structure, the responsibility, and the authority for each activity.
- Overview of Quality Document Management (including the document name and information to help identify the latest revision status): The manufacturer should submit a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) to demonstrate the establishment of an overall QMS for requirements in accordance with the Medical Device Manufacturing and Quality Management Standards. In scenarios where a manufacturer falls under the “manufacturer requestor-manufacturer,” they must prepare the document in connection with the application for medical device conformity examination, etc. Sub-documents such as work instructions, records, forms, etc., may be excluded.
- The Standard Checklist of the Manufacturer: This data is used to minimize the differences between on-site investigation and document review by checking the application and its compliance with the requirements of the Medical Device Manufacturing and Quality Management Standards. Each requirement is reviewed for applicability and compliance and submitted with information from the same documented SOP as the Submittal Quality Documentation Management Overview. The plant’s personnel shall prepare the reference checklist of the manufacturing plant, which is subject to examination and must include the signature of the QMR or a person with the same responsibilities and authority.
- Declaration of Conformity to the Standards of the Manufacturing Plant: The manufacturer needs to confirm its efforts and willingness to manufacture safe and appropriate-quality medical devices by declaring that it has established, executed, and maintained a QMS in accordance with the requirements of the Medical Device Manufacturing and Quality Management Standards. The personnel at the plant shall prepare this section, which is subject to examination and includes the signature of the QMR or a person with the same responsibilities and authority.
- A Summary of Validation of the Production and Service Delivery Process of Representative Items in the Manufacturing Plant: Process validation is extremely important to prevent risks that may occur during the production and service processes. However, the process validation data are limited to the major processes and facilities related to the manufacture of representative items due to the extensive scope and data, and the manufacturer needs to prepare and submit a summary data of the validation.
The period during which data submission is required is as follows, and the history of process validation beyond the specified period shall record plausible reasons (first and additional review).
- A summary of the most recent activities in relation to the items (change review).
- A summary of activities conducted in the last three years as of the date of application for review.
The importer may submit data for imported medical devices based on a foreign manufacturer’s data (letters, documents, etc.).
- Management Summary Data: The manufacturer needs to submit the data of monitoring and measuring equipment of the manufacturing plant and management summary data only for major equipment related to the manufacturing of representative items.
- Designation of Innovative Medical Devices for Representative Items: The requirement is limited to innovative medical device software. Article 21 of the Medical Device Industry Development and Innovative Medical Device Support Act, Article 15 of the Enforcement Decree of the same Act, and Article 2, Paragraph 2 of the Rules for Supporting and Managing Innovative Medicines shall apply and (Appendix 2 Form) shall be submitted.3
This information is accompanied by a certificate demonstrating that the submission data is prepared by/for the manufacturer. The certificate shall include the following details:
- A full list of submission documents (the name of each document, version [if applicable], and document number).
- The date of affiliation/position/signing and certification of the QMR or a person with equivalent responsibility and authority.
- Contact information for verifying the contents of this certificate (phone number/email, etc.).
The MFDS has revised the Medical Device Manufacturing and Quality Management KGMP Standards three times between 2020 and 2021. Earlier, manufacturers preferred the KGMP document audit. However, since the revised requirements have been put in place, document audit preparation and the corresponding KGMP audit have become much more difficult, and even the global top-tier medical device manufacturers are now struggling with KGMP audits. Since on-site audits are resuming this year, it is important to stay on top of real-time trends, as the documentation requirements are demanding, and all four agencies have different audit schedules. Ultimately, the key to a successful KGMP certification is to get help from experts and familiarize yourself with the new KGMP requirements.
References
- Medical Device Act (MFDS February 18, 2022).
- Enforcement Decree of the Medical Device Act (MFDS February 18, 2022).
- Medical Device Manufacturing and Quality Control Standards (MFDS February 10, 2022).
- Medical Device Quality Manager Training Material and KGMP Guideline by MFDS (2016, 2022).
 About The Author:
About The Author:
Kang-Keun Lee is the domain expert for South Korea medical devices regulations at Freyr Solutions and has spent more than 10 years leading numerous Korea device approval projects. He has experience in quality management systems, KGMP procedures, CAPA, and post-market surveillance of medical devices, including imaging- and AI-based medical devices. He has played a major role in devising quality and regulatory strategy for medical devices and IVD companies.

