The Growing U.S. Market For Endoscopic Gastrointestinal Devices
By Hadi Salempoor and Kamran Zamanian, Ph.D., iData Research Inc.
Gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopes, which are flexible instruments used for visualizing and performing procedures in the GI tract, play a crucial role in diagnosing conditions and conducting less invasive surgeries.
Beyond visualizing the GI tract, these endoscopes facilitate less invasive surgeries by carrying instruments like forceps and hemostasis devices into the digestive tract. Ongoing technological advancements have made GI endoscopes smaller and more efficient, employing technology akin to that used in televisions and computers. The widespread use of high-definition (HD) technology, coupled with reductions in chip size, has expanded the scope of applications for GI endoscopes, with fiber optics and improved image quality opening new possibilities. Medical professionals see the following advantages in these devices:
- Efficient pain management: The tools excel in minimizing patient discomfort during procedures, allowing doctors to perform their tasks seamlessly while prioritizing patient well-being.
- Precision in diagnosis: Equipped with advanced cameras, these devices deliver a clear and detailed view of the internal landscape, enabling doctors to detect and address potential issues early on, thereby enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
- Technological excellence: Endoscopic tools continually evolve with cutting-edge technology, incorporating superior cameras and innovative problem-solving approaches. These advancements ensure that these devices remain at the forefront of medical innovation, providing physicians with increasingly effective means of diagnosis and treatment.
The GI endoscope market in the U.S. currently holds a value of around $1.2 billion, and it is projected to reach close to $1.5 billion by the end of the forecast period (2030), indicating an impressive growth rate with a CAGR of approximately 3.1%.
This article provides an overview of the dynamic market landscape and explores the latest trends in the market and the influence of COVID-19.
Market Trends And Drivers
The GI endoscope market includes reusable colonoscopes, reusable sigmoidoscopies, reusable duodenoscopes, single-use duodenoscopes, single-use cholangioscopes, reusable enteroscopes, reusable ultrasound endoscopes, reusable double-balloon endoscopes, reusable and single-use gastroscopes, single-use choledochoscopes, single-use duodenoscopes, single-use cholangioscopes, and third-party refurbished endoscopes.
In 2023, the largest segment of the GI endoscope market was the reusable colonoscope market. The relatively large size of this segment is attributed to the large annual volume of colonoscopy procedures.
The second-largest segment was the reusable gastroscope market. Again, the relatively large size of this segment is attributed to the large annual volume of upper endoscopy procedures. The third-largest segment was the ultrasound-endoscope market; growth of this market is driven by an increase in endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) procedures.
The remainder of the market was accounted for by the single-use cholangioscope, reusable double-balloon endoscope, reusable duodenoscope, single-use duodenoscope, third-party refurbished endoscope, and sigmoidoscope markets.
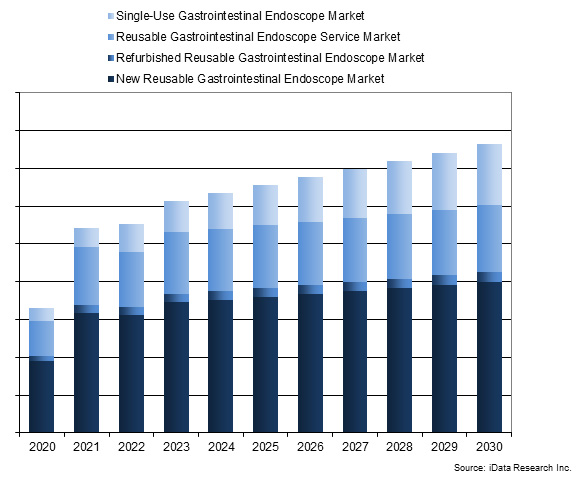
Figure 1: Access iData’s U.S. Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Device market report to view more granular data.
Incidence of Cancer
According to the American Cancer Society, there were approximately 106,970 cases of colon cancer and 46,050 cases of rectal cancer in the U.S. in 2023.2 According to the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE), colorectal cancer is the third-leading cause of cancer deaths (after lung cancer) in the United States.3 Over the past decade, media campaigns initiated by cancer awareness organizations and governmental bodies have done a lot to increase awareness of the condition and the necessity of screening for it. The stigma attached to the procedure also has been drastically reduced, and many people realize that a colonoscopy every five to 10 years can greatly reduce their chances of developing cancer. With the ongoing support from GI lobbying groups, the growth in screening programs will continue to positively contribute to the market.
Technological Advancement
Technological advancements and product improvements over the past several years have made GI endoscopes more effective in performing GI procedures. The HD format and now HD+ along with advanced magnification capabilities, which penetrated the GI endoscope market only recently, resulted in a greater detection rate for polyps. Improved designs also have made flexible GI endoscopes easier to handle, and smaller instrumentation has allowed for more specialized devices. As of 2023, the research and development agenda included improved mobility and guidance, improved reprocessing, artificial intelligence assistance, and improved 3D and 4K capabilities. New reusable scopes are poised to benefit the most from technological advancements. Without needing to focus efforts toward cutting costs the way their single-use counterparts do, new scopes seek out a competitive edge by implementing cutting-edge technology.
The evolution of endoscopic technology closely aligns with advancements in computer technology. Distal chips and HD/full high-definition (FHD) technology enhance image quality, enabling more accurate diagnoses by physicians. The average lifespan of an endoscope is five years, influenced by usage frequency and care. While some endoscopes can last up to 10 years, others may need replacement after three years. Varieties like colonoscopes, being more robust, often have slightly longer lifespans. Care significantly impacts endoscope lifespan, with complete cleaning requiring industrial chemicals that can damage the scope. Increasing awareness of cross-contamination prompts rigorous cleaning practices to avoid chemical-induced damage. To address infection risks, single-use technology is under development.
Amidst an aging population and a focus on early disease screening, GI endoscopes are poised for continued advancements, emphasizing efficiency and technology. As technology propels healthcare forward, endoscopic gastrointestinal tools play a crucial role in improving diagnostic accuracy and enabling less invasive procedures. The ongoing pursuit of smaller, more efficient endoscopes reflects a commitment to enhancing patient care. The trajectory of GI endoscopes suggests a future marked by continual innovation and increased efficiency. In navigating this evolving landscape, healthcare providers, manufacturers, and investors stand to contribute to the ongoing transformation of gastrointestinal care in the United States.
COVID-19’s Impact On The GI Endoscope Landscape
COVID-19 has significantly impacted the landscape of endoscopy procedures. Ensuring timely, secure, and effective access to the GI tract for patients infected with COVID-19 poses unique challenges, necessitating careful consideration to minimize the risk of viral transmission to healthcare professionals and the surrounding equipment. Recent research indicates variations in endoscopic procedures between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 patients (patients with COVID-19 often required different endoscopic procedures due to infection control measures, such as increased use of personal protective equipment, negative pressure rooms, and pre-procedure testing for COVID-19), emphasizing the need for adapted approaches in these critical situations.1 Endoscopes play a pivotal role in achieving successful diagnostic and therapeutic interventions with reduced complications. Their precision and extended capabilities contribute to minimizing procedural risks and enhancing overall patient outcomes. As the healthcare industry continues to navigate the challenges posed by the pandemic, the demand for innovative endoscopic solutions is on the rise, reflecting a paradigm shift in the approach to patient care.
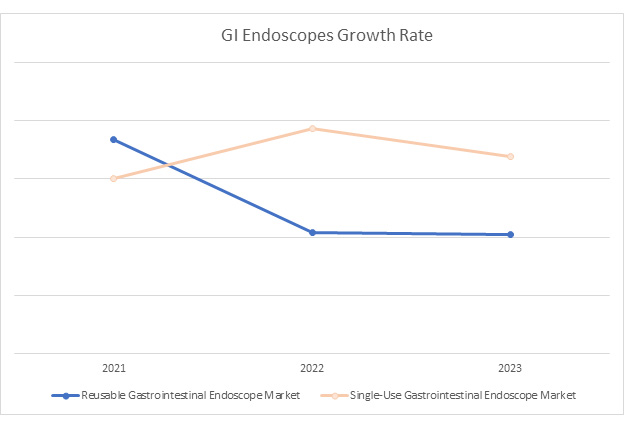
Figure 2: Single-Use Gastrointestinal Endoscopes and Reusable Gastrointestinal Endoscopes Market Value in 2021, 2022 and 2023. Access iData’s U.S. Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Device market report to view more granular data.
Closing Thoughts
The evolution of gastrointestinal endoscopes, from facilitating less invasive surgeries to incorporating advanced imaging technologies, aligns with the dynamic needs of the medical field.
The robust market growth, with a projected CAGR of approximately 3.1%, underscores the pivotal role these devices play in diagnosis and treatment. The ongoing technological advancements, symbolized by distal chips, HD/FHD technology, and innovative problem-solving approaches, signify a commitment to excellence in patient care.
Amidst an aging population and a heightened focus on early disease screening, the trajectory of GI endoscopes points toward continual innovation and increased efficiency.
References
- Ucl. (2022, May 6). COVID-19: Backlog of half a million endoscopies and rising. UCL News. https://www.ucl.ac.uk/news/2021/mar/covid-19-backlog-half-million-endoscopies-and-rising
- Colorectal cancer statistics | How common is colorectal cancer? (n.d.). American Cancer Society. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
- Patient information. (n.d.). www.asge.org. https://www.asge.org/home/for-patients/patient-information/understanding-colonoscopy#:~:text=Colorectal%20cancer%20is%20the%20third%20leading%20cause%20of,
would%20save%20at%20least%2030%2C000%20lives%20each%20year. - iData Research Inc. U.S Gastrointestinal Device Market – 2024. https://idataresearch.com/product/gastrointestinal-endoscopic-devices-market-united-states/
 About the Authors:
About the Authors:
Hadi Salempoor is a research analyst at iData Research. He works on research projects regarding the medical device industry, publishing the U.S. Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Device market research report.
 Kamran Zamanian, Ph.D., is CEO and founding partner of iData Research. He has spent over 20 years working in the market research industry with a dedication to the study of medical devices used in the health of patients all over the globe.
Kamran Zamanian, Ph.D., is CEO and founding partner of iData Research. He has spent over 20 years working in the market research industry with a dedication to the study of medical devices used in the health of patients all over the globe.
