Unlocking Business Value In Digital Health Solutions In Pharma
By Sierra Nesbit and Stephen Morehouse, PA Consulting

Now more than ever, pharma companies face intense pressure to accelerate the speed of innovation and are seeking new ways to distinguish themselves. Digital solutions provide a unique opportunity to differentiate — delivering new value to patients along their treatment journey, strengthening the core business, and accomplishing desired innovation goals.
These solutions have the power to elevate and enhance the current standard of care by improving clinical outcomes, boosting healthcare professional (HCP) and patient experiences, and creating dynamic personalized care. Digital products are a growth area that more and more companies continue to pursue and iterate on, unlocking new ways to support patients. Examples include companies such as Pfizer and Lilly, which have recently introduced direct-to-consumer medicines platforms complete with educational information, mail order pharmacy services, and access to telehealth providers to partner with patients on their treatment journey.
These solutions added value across all parts of the value chain (payers, providers, and patients) through drivers such as a shift in site of care and lowering overall healthcare costs. This article will explore the ways companies are unlocking incremental value through digital solutions, employing the right strategies at the right time to prepare for a successful product launch.
To successfully launch a digital health solution, pharma companies can focus on three key areas:
- Value demonstration — How can your organization measure and communicate the value of digital solutions to increase uptake and engagement? What are the market access needs and requirements for specific solutions, and what benefits can be achieved in meeting them? Does your organization have a clear understanding of the target user's need and the role digital will play in the patient journey and existing patient programs? How does your organization leverage data to enhance product development and create better solutions?
- Key capabilities and functionality required for digital solutions — Does your organization have the right digital expertise and capabilities in place across all pharma functions, as well as user experience, human factors, safety, cybersecurity, and data privacy, to successfully build and operate a digital solution? Does your organization have the right infrastructure in place to host a digital health solution and associated data? How will your organization operate efficiently across key functional areas such as personal data, IT, safety, commercial, regulatory, and medical?
- Partnerships and collaboration — Should your organization proceed independently or consider a strategic partner to support digital solution development and launch? Can your organization enable a hybrid model outsourcing certain elements to accelerate development in digital-specific expertise? Which functions in your organization require the most support around digital solutions? Should your organization leverage a hybrid model to mature internal capabilities for digital solutions in the future?
Value Demonstration
Digital solutions deliver differentiated value to all stakeholders involved in the patient journey. Traditionally, the value proposition for digital has focused on the patient, enabling higher quality of life by allowing seamless administration of treatment, reducing travel to the doctor’s office, and providing the ability to self-manage health. These digital solutions also create significant bottom-line impact for both providers and payers, helping them to curb costs and improve outcomes. For providers, digital solutions create operational effectiveness by shifting low-acuity patients to lower-cost sites of care such as outpatient clinics or the home, as well as leveraging remote monitoring systems to provide continuous, real-time patient data to improve clinical decision-making and patient outcomes. For payers, digital solutions act as tools to steer members away from less cost-effective treatment options, reduce over-utilization and waste (i.e., better clinical decision-making leads to personalized treatment regimens), and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations and readmissions by catalyzing faster intervention.
Companies need a strong grasp of the value equation and ROI early in the development life cycle. Unfortunately, many have struggled to achieve their full market impact post-launch due to a lack of clarity from the outset. However, a few companies that are no longer in operation, including Better Therapeutics, Pear Therapeutics, and Proteus Digital Health, developed exceptional digital products that added real value to patients but had several shortcomings in areas like business strategy, scalability, or user adoption. These instances offer some important lessons for the industry to learn from and consider moving forward.
Top 5 Learnings From Early Digital Health Leaders
- Understand the patient journey — Assess how the solution will add differentiated value and shape the care delivery landscape, including HCPs, payers, and other influencers of solution adoption.
- Strong clinical evidence generation — Establish meaningful clinical endpoints and a clear value proposition to support provider adoption and payer negotiations.
- Robust reimbursement strategy — Explore payment models, considering both the pathways and timing for leveraging them, while recognizing that CPT codes may not always be available during solution development and require crafting a strategic approach for pursuit.
- Consider alternative revenue generation approaches — A direct-to-consumer route is one possible approach as there may be instances where consumers are willing to pay out of pocket for solutions when they realize the product’s value.
- Recognize investment required for adoption and retention — Invest energy in the targeted marketing efforts and service activities that showcase the value of the solution to all stakeholders along the patient journey (i.e., HCPs, patients, providers, and advocacy groups) to both enable solution adoption and retain users post-launch.
Looking forward in the market, companies must continue to iterate and enable digital products that will shape the patient’s experience along the care pathway through creative tools such as AI-driven treatment plans, decentralized clinical trials, and virtual health assistants.
Digital solutions provide the opportunity to collect valuable data points that benefit all stakeholders involved in patient care, even when future uses for that data are not immediately clear. Companies can collect key data points around adherence, drug efficacy, symptoms, and patient preferences by putting digital services in place. By gathering this information, we can develop better products, enhance customer relationships, and adapt more effectively to evolving healthcare needs.
Key Capabilities And Functionality Required For Digital Solutions
Companies continue to explore opportunities to enable digital, but solutions are not always embedded in the care pathway to a degree that is meaningful in a patient’s journey. For digital to transform care delivery across the value chain, organizations must have the right capabilities in place. With a projected market volume of $10 billion by 2029 for the digital therapeutics market alone, companies need to assess which model is right for them as they integrate digital into care delivery. The right model should meet their existing needs while providing the capabilities necessary to deliver incremental value through digital innovation — allowing organizations to further differentiate themselves in the market.
Companies vary widely in their experience with digital solutions. Most traditional models center around building digital solutions in-house and leveraging existing infrastructure and resources. Given the novelty of these technologies, many organizations must invest significantly in establishing new capabilities for digital solution development like user experience and human factors. But this investment pays off. Combining clinical trials with digital telemonitoring solutions can increase drug efficacy; in 2019, the ‘TeleDiab‐2’ controlled trial evaluated the efficacy of telemonitoring systems to optimize basal insulin initiation in patients with type 2 diabetes. A combination of digital therapeutic (Diabeo-BI) and telemonitoring was compared against a simpler telemonitoring device group as well as a control group receiving standard of care. The fasting blood glucose objective of 100mg/dL was reached by twice as many patients in the interventional group as in the control group. This positive experience led 98 percent of patients using a combination of digital therapeutic (Diabeo-BI) and telemonitoring to request continued use.
Partnerships And Collaboration
Stakeholders across the industry are looking to be innovative and quickest to launch, all while proving their efficacy and value in the market. Strategic collaboration with digital solution partners can alleviate many of the challenges and provide pharma companies with the opportunity to gain a competitive edge. Many organizations have attempted to develop digital solutions in-house but struggle to activate the right business model to enable value. Ambiguity over product ownership and navigating the regulatory landscape have led companies to question the value of pursuing digital as a viable revenue stream altogether. Creating and managing digital health solutions demands years of expertise from digital health companies to quickly design, develop, and commercialize solutions that meet pharma's business needs and users' clinical requirements. Below are some of the drivers that companies should assess when considering a strategic partnership (see Figure 1).
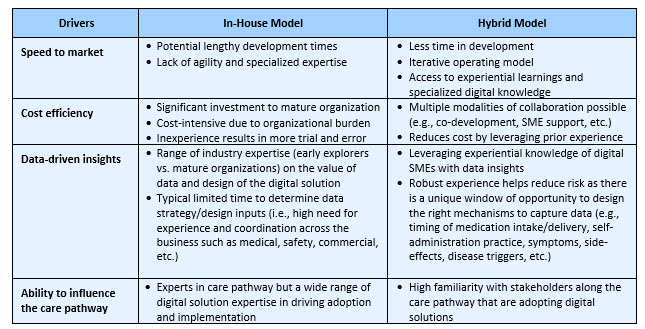
Figure 1: Traditional in-house models versus hybrid partnership models
Strategic partnerships enable companies to enhance therapies via digital solutions that reach patients and providers in shorter timelines. For example, Aptar Digital Health partners with strategic pharma and biotech companies to address patient needs using digital health solutions, leveraging cross-organizational expertise. These partners harness clinical endpoints to advance therapies in areas like immunology, oncology, and rare diseases, while others like Huma and Vantis apply technologies such as remote monitoring and chronic disease management to improve outcomes like adherence and reduced readmissions.
Digital is here to stay, and companies risk falling behind if they don’t advance their organizations to mature digital solutions. One strategy that companies are taking to accelerate their digital solutions, reduce risk, manage cost, and mature internal capabilities is through leveraging a hybrid model. Many companies remain skeptical of the value that digital can provide given prior industry failures and unknowns around how these assets generate revenue. Many high-value concepts fail to progress as companies struggle to calculate the ROI of digital solutions and justify investment to leadership. However, we should not look to this as the rationale to forgo greater opportunities that are outside the bounds of typical development stage gate criteria. Several products are beginning to crack the value equation and ROI, creating a competitive edge through the value of data, ability to accelerate digital solutions via hybrid models, and impact the care pathway to enhance patient care.
 About The Authors:
About The Authors:
Sierra Nesbit is a healthcare expert at PA Consulting specializing in operating model and business design, project management, agile methodologies, and strategic road mapping.
 Stephen Morehouse is a life sciences expert at PA Consulting with 30 years of experience in expertise across pharmaceuticals, biotech, and diagnostics. Throughout his career, Morehouse has supported large pharma companies, investment firms, and startups in the U.S. and Europe with growth strategies and technical and commercial assessments.
Stephen Morehouse is a life sciences expert at PA Consulting with 30 years of experience in expertise across pharmaceuticals, biotech, and diagnostics. Throughout his career, Morehouse has supported large pharma companies, investment firms, and startups in the U.S. and Europe with growth strategies and technical and commercial assessments.
